HIV AND AIDS
When it comes to HIV and AIDS, we generally have lots of queries
in our minds regarding it. In this article, we provide you information about HIV,
AIDS, its risks, and how to lower the same.
 |
| WHAT IS HIV/AIDS? |
What is HIV?
HIV i.e. “Human Immunodeficiency Virus” is a virus that attacks
cells that help your body to fight against infections. In simple words, HIV The virus damages your immune system.
Untreated HIV leads to AIDS i.e. acquired immunodeficiency
syndrome.
Unfortunately, it does not have an effective cure for it, but with proper
medical care can be controlled.
What is AIDS?
AIDS is the advanced stage of HIV. In this stage the immune system
of your body gets badly damaged because of the virus.
HIV kills CD4 cells present in your body. Normal Healthy people
have a CD4 cells count of about 500 to 1,600 per cubic millimeter. But a person
with AIDS has their CD4 cells below 200 cells per cubic millimeter of blood
(200 cells/mm3).
AIDS makes the person vulnerable
to a wide range of illnesses. Without treatment of AIDS, a person can survive for
about 3 years only.
So the diagnosis of it is very important.
How is HIV Transmitted?
HIV Virus is transmitted through fluids present in our body:
- semen
- blood
- breast
milk
- blood
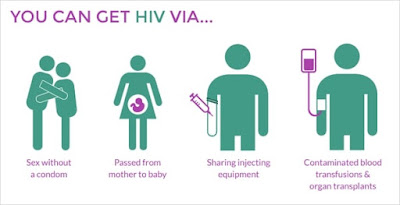
What are the ways HIV is transferred from one person to another?
HIV is transferred from a person to another in the following ways:
- Having
vaginal or anal sex - Using
infected needles, syringes for injecting drugs - During
breastfeeding - During
Pregnancy to the baby - By
chewing baby’s food before feeding it to them - Blood
or organs transfusion - Tissue
transplant
You should not confuse about the myths about the transmittance of HIV.
It does not get transmitted through:
- Hugging
- Kissing
- Shaking
hands - Air
or water - Saliva,
tears, or sweat (only when not mixed with blood) - Sharing
bed, towels, or toilets - Mosquitoes
- Sharing
food or drinks
What are the stages of HIV?
Acute
stage:
- In this stage, people have a large amount of HIV in their blood. Some may experience flu-like symptoms or may not feel sick at all.
It can be diagnosed by antibody tests
or nucleic acid tests (NATs).
Chronic
Stage:
- The chronic stage is also known as clinical latency. In this stage HIV is active but it gets reproduced at
very low levels.
At the end of this phase, the amount
of HIV in the blood goes up and the CD4 cell count goes down.
By taking HIV medicines, you would
not enter Stage 3 of HIV.
AIDS
(Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome):
- This is the last stage of HIV.
People at this stage have badly
damaged immune systems and get an increasing number of severe illnesses, called
opportunistic infections.
The amount of HIV in the blood is
very high and the person could be very infectious.
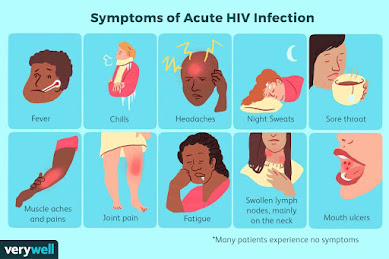
What are the symptoms of HIV?
Some of you may or may not experience HIV symptoms at chronic
stage. Some of the nonspecific symptoms are listed below:
- night
sweats - headaches
- fatigue
- vomiting
- weight loss
- pneumonia
- recurrent fevers
- vaginal yeast infections
- swollen
lymph nodes - diarrhea
- skin
rashes
How to know if you have HIV?
The only possible way to know if you are HIV positive is to get
tested.
You can also go for self-testing at home by buying testing
kit.
What are the tests performed for HIV?
Antibody
or Antigen Test:
- This is a common test for checking
the blood for antibodies and antigens and the results of it are obtained
within 18–45 days after someone initially bears HIV.
Nucleic
Acid Test:
- This test is performed to detect
HIV virus in the blood.
This test takes the duration of about
5-21 days to be performed.
What are the Symptoms of AIDS?
Those people who are not diagnosed with HIV develop AIDS.
Here are the symptoms of AIDS:
- Chronic
fatigue - Rapid
weight loss - Anxiety
and depression - Recurrent
fever - Chronic
swollen lymph glands - Sores,
spots on the mouth and tongue, genitals - Chronic
diarrhea - Neurologic
problems
You should get diagnosed in proper time as it helps to prevent
AIDS from getting progressed.
What is the Treatment for HIV?
The treatment for HIV is antiretroviral therapy. It helps to
prevent the virus from reproducing.
It protects your CD4 cells and makes your immune system
strong so that it can fight against various diseases.
This effective treatment reduces the risk of transmitting HIV to
others.
You should never stop this treatment after starting it as the HIV
in the blood may start increasing and it further will be destroying your CD4
cells.
What are the medications used for HIV?
There are antiretroviral therapy medications that are used to
treat HIV.
The antiretroviral therapy medications that are used are
- Non-nucleoside
reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs) - Protease
inhibitors - Fusion
inhibitors - Nucleoside
reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs) - Integrase
strand transfer inhibitors - CCR5
antagonists
You should strictly consult your doctor before opting for any of
the above medicines.
What are the Side Effects related to it?
There are many side effects of antiretroviral therapy experienced
depending upon one person to another. Sometimes these side effects may become
serious.
The side effects include headache, dizziness, nausea, etc.
The serious side effects include kidney damage, swollen liver,
swelling of tongue, mouth, etc.
How can you prevent HIV?
There are much research’s going on for developing vaccine for HIV
but till now it has not been developed. So you should take steps to prevent
HIV.
1.
Safe Sex: Anal sex or vaginal sex is
the most common way of transmitting the HIV virus. So you should perform safer sex
with your partner by correctly using condoms. Do remember that there are
pre-seminal fluids present in the body that may contain the HIV virus.
2.
Get Tested: You should always have a
check of HIV and of your partner too.
3.
Test STI’s: Do test if you have any
STI’s increases the risk of contracting HIV. Get treated as soon as
possible.
4.
Take medications: If you are tested
positive for HIV then take the medications as directed by your doctor.
5.
Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP): It
is a combination of two drugs that are available in pill form. If it is taken
consistently it can lower the risk of transmitting the HIV virus.
How can
you cope up with HIV?
Following are the tips to cope up
with HIV and to lead a happy and normal life:
·
Take care of your health: You should
make your health to be the first priority. Eat a balanced diet, do some regular
exercises drink water, take rest and avoid consuming drugs to lead a better
life.
·
Do not get over-stressed.
·
Practice sex with your partner safely
by using effective measures.
·
Spend time with your loved ones.
·
Get support if required of counselors
if you find yourself in very difficult situations.
Frequently
Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
1.
Will HIV transmission occur if both
the partners are HIV negative?
No, if both partners are HIV negative, then the transmission cannot occur.
Two partners having sex without a condom need to trust that neither partner
could catch HIV outside the relationship.
2. Can the sex be performed without
condoms?
HIV
negative people can have sex if:
They
both are tested HIV negative and are prone to no risk.
You are
not concerned about pregnancy
You do
not have any risks of having STI’s.
3. What to do if one partner is positive
and one is negative?
If one of you is HIV positive and another one is HIV negative, you need to be careful
to reduce the risk of HIV transmission. While having sex you should use
preventive measures to avoid the risk of the HIV virus.
Also
the one with HIV negative can use PrEP to make the risk of transmission
completely zero.
4. Will the other partner will also be HIV positive if he/she has sex
with an HIV-positive partner although he/she is getting diagnosed?
No, if
the HIV partner is getting diagnosed then there are reduced risks of the other
one of getting HIV positive.
5. Can I become HIV transmitted without
having sex also?
Yes,
you can become HIV transmitted as HIV can also pass from mother to child during
pregnancy, childbirth, or breastfeeding.
6. How can I protect myself from HIV?
If you
decide to have sex, reduce your risk of getting HIV by:
·
using a condom every time you have
sex (including vaginal, or anal sex)
·
getting tested for HIV and making
sure all partners do too
·
reducing the number(stick to your
only one trusted partner) of sexual partners you have
·
getting tested and treated for STDs
(sexually transmitted diseases) as having an STD increases the risk of HIV
infection

Leave a Reply