How to format kidney stone and what are the steps to prevent stone?
Kidney:
The kidneys are vital organs which filter the blood and produce
urine urine is composed of water urea and excess ions it leaves the kidney via
the ureter and is stored in the bladder until it is eventually excreted.
Because urine contains ions that can form salts these salts
can crystallize informants what I refer to as stones or Kelsey which can then obstruct
components of the urinary system.
Urolithiasis is a term that refers to stones forming
in the urinary tract the word lith comes from Greek and means stone.
1.A stone located in the kidney is known as nephrolithiasis or renal calculi.
2. If the stone is located in other parts of the urinary
tract such as the ureter or bladder then is known as ureteral Ephesus or
systole fascist.
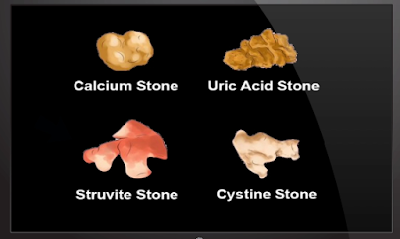
Primary types of kidney stones:
- The most common to least common are calcium containing
stones including calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate.
- Magnesium ammonium phosphate also called struvite or
staghorn stones.
- Uric acid stone
- Cysteine stone
- Xanthine stones which are quite uncommon.
- Calcium phosphate and struvite stones are more likely to
form in basic urine. - While uric acid and
cysteine stones are more likely to form an acidic urine. - Calcium oxalate stones
may form in either alkaline or acidic urine.
Three major steps
in the formation of kidney stones:
- Nucleation
- Growth
- Aggregation

Nucleation refers to ions such as calcium and oxalate coming
together to form a solid crystal nightís and this most often occurs in the
collecting ducts. these crystals are dumped into the renal papillae where they
grow in size in the renal pelvis the crystals will aggregate with one another
to form larger crystals and stones at this point they may leave the renal
pelvis and travel into the ureter.
The ureters are 3 to 4 millimeters in diameter. if the
stone is for example 5 millimeters it won’t easily pass down the order and
will elicit the characters of painful renal colic as it irritates the ureter especially
during intermittent dur peristaltic movements renal colic is the pain
associated with the ureter stone.
There is a continuous pain but excruciating waves of pain
come on intermittently as periodic peristaltic ureter contractions attempt to
force the stone down the ureter. this colicky pain occurs in the lower back and
flank region on the affected side and may radiate through the abdominal region
and down to the drone groin area intense.
- Colicky pain is often associated with nausea and vomiting in
contrast non colicky pain is continuous and is typically not as intense and is
associated with a stone being in the renal calyce’s or renal pelvis.
- Unlike colicky pain non colicky pain increases with
movements so patients attempt to remain very still non colicky pain is similar
to that associated with appendicitis or pancreatitis.
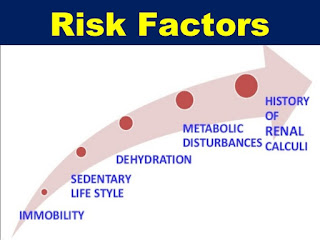
There are many risk
factors for kidney stone formation:
- Including stone forming constituents such as calcium
oxalates taking calcium supplements or regularly using calcium containing
antacids increases the risk for calcium stones. - Oxalates are found in spinach Swiss chard,cocoa, pecans, peanuts, soy products and other foods and increase the risk for calcium oxalate
stone formation. - Magnesium ammonium phosphate stones for more commonly in
women and especially in those with recurring UTIs certain bacteria use the
enzyme urease to convert urea into ammonia which is basic the now more alkaline
environment increasing increases phosphate in the urine which combines with
ammonium and magnesium ions to form the stones. - Urate stones form more commonly in those that have high plasma
levels of uric acid or hyperuricemia a drug use for gal called probenecid
blocks URI reabsorption in the PCT and will decrease urate levels in the urine
which also increases the risk for your a stones for this reason it is
especially important to drink lots of water while taking probenecid.
Pharmacologic treatments for kidney stone:
- For ureteral ethicist Tamsulosin and Alpha 1 a antagonist can be used to help dilate the usurer and
help the stone pass a strong inside.
- Like ketorolac or opioids
such as hydromorphone or morph morphine may be used for the intense colicky
pain.
- Tiny Asya drugs like ondansetron and promethazine may be
used to treat nausea and vomiting.
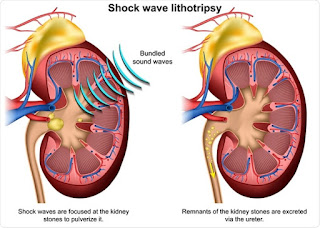
- Shock wave lithotripsy (SWL):
shock wave lithotripsy is a non-surgical technique that may
be used for removal of kidney stones. the patient is positioned in a water bath or lies on a cushion.
it is painful so it’s
generally done under anesthesia SWL involves the use of shock waves which are
high-frequency sound waves or ultrasound that is targeted at the stone breaking. it up SWL is useful for stones smaller than 30 millimeters and is not used for Cysteine stones.
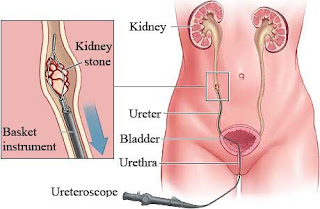
2. Ureteroscopy:
Ureteroscopy is ideal for medium sized stones in ureter this procedure is
also done under general anesthesia and involves inserting a flexible durable
ureteral scope into the bladder and then up into the ureters a laser or
pneumatic device is then used to pulverize the stone under vision.
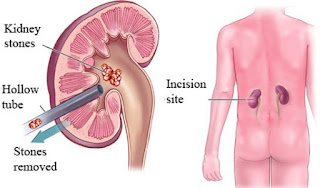
3. Percutaneous nephrolithotomy:
where a small hole is made in the back to access the kidney
a camera is inserted through the hole and allows for a visualization of the
stone which is then pulverized using ultrasound lasers or a pneumatic device.
So how do you know if you have a kidney stone?
- pain in the right or left side of your back.
- some nausea and possibly vomiting associated with this pain.
- you may even have some fever and on rare occasion chills with this discomfort.
- you may also notice that there’s blood in your urine.
How to prevent kidney stone:
- There’s nothing more important than drinking a lot of fluid.
- The average kidney stone patient needs drink at least 3 quarts of fluid a day in order to make 2.5 courts of urine a day. Once you’re doing that, the chance of any recurrence stone disease drops by over 50%. This is more important than any medication you can take or any diet.
- To drinking enough fluid is your diet.
- You should have a normal calcium diet, usually 1 gram a day, a low-salt diet usually no more than 2-3 grams a day, and low animal protein less than 50 grams a day.
All of this will help prevent a recurrent kidney stone, but again diet is secondary to drink.
Finally if you have more than one stone, you should see a urologist for full metabolic evaluation and treatment plan to prevent recurring stones.
I think you definitely understand about kidney stone and this information helps you. If you want to know about other health problems so visit these pages it will helps you.


Leave a Reply